Proposed Designs for James Webb Space Telescope
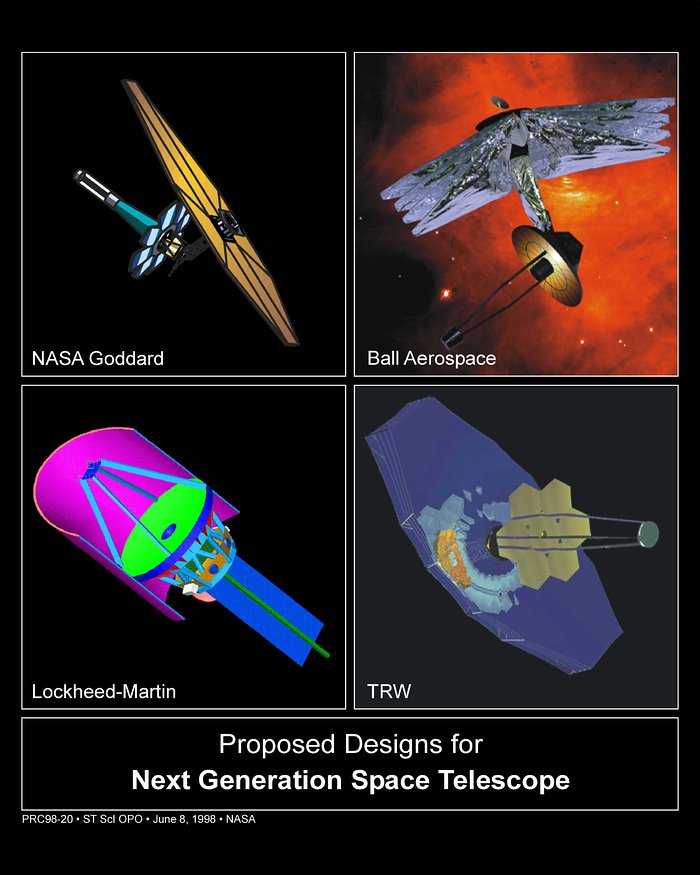
Upper left: The Goddard Space Flight Center-led team developed this lightweight design for JWST. It incorporates many of the features found in the other designs: a deployable, 26-foot-wide (nearly 8 meters) primary mirror, a large deployable sunshade to shield the optics, and an orbit 930,000 miles (1.5 million kilometers) from Earth at the L2 Lagrangian point, a balancing point between the gravitational tug of the Earth and the Sun. The spacecraft has a deployable sunshade, an umbrella that will keep the telescope chilled -370 degrees Fahrenheit to -298 degrees Fahrenheit, which allows it to see the faint infrared glow of distant objects. With this design, the telescope can view about 40 percent of the sky at any time.
Upper right: This design by Ball Aerospace features four widely separated sunshields that are effective in reducing the temperature of the telescope optics and the science instrument compartment. The deployable primary mirror is mounted on three hinged slices of a 26-foot (8 meters) circular structure. By rolling the spacecraft so that the sunshade is always perpendicular to the Sun, the telescope can view half of the sky. The Ball model is designed for launch to L2 or similar orbits.
Credit:About the Image
About the Object
| Name: | James Webb Space Telescope, JWST |
| Type: | Unspecified : Technology : Observatory : Telescope |
| Category: | Illustrations James Webb Space Telescope |